Implementing SAP Activate Roadmaps guides SAP S/4HANA innovation projects to well architected cloud architectures.
SAP Activate Roadmaps guide technical workstreams with best practices to implement excellent SAP S/4HANA Cloud Architectures.

These best practices follow well architected cloud frameworks to adapt SAP S/4HANA Public or Private Cloud solutions deployment specific.
Technical Discovery topics like system landscape setup, release management or sizing are specific to S/4HANA Public or Private Cloud deployment options and have to be aligned with the respective contractual conditions. Default SAP S/4HANA multi-tenant and single tenant cloud landscapes consist of three systems. SAP S/4HANA Single tenant private cloud system landscapes can be extended with additional costs.
Main sizing criteria for SAP S/4HANA system environments are Full User Equivalent (FUE) metrics. Additionally, capacity requirements of Embedded Analytics, Business AI, API Frontend Network Load or concurrent user sessions have to be considered. SAP S/4HANA brownfield transformations offer additionally sizing based on existing data volumes.
Initial system access to S/4HANA Public or Private Cloud systems has to be requested. Further access to systems like SAP Business Technology Platform (SAP BTP), SAP Cloud ALM or SAP Cloud Analytics has to be initialized.
Technical architectures for S/4HANA Public or Private Cloud editions (PCE) need to be defined with cloud architecture best practices and the integration of additional SAP SaaS or PaaS solutions like SAP CALM or SAP BTP.
The SAP Activate data management workstream has to deliver a Data Migration Strategy with defined milestones, scope, tools, volumes and data processing steps. Data sizing shall be prepared with data reduction by archiving no longer needed business data and the deletion of outdated data.
Important preparation tasks for SAP S/4HANA system conversations are readiness or simplification item checks and to establish custom code quality management.
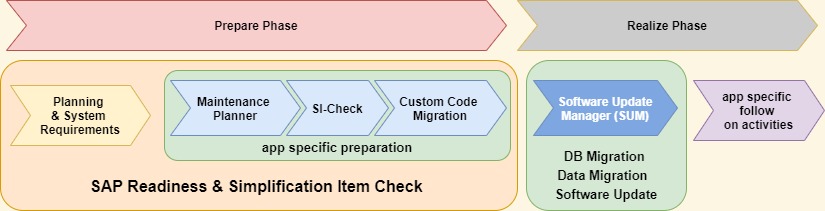
SAP S/4HANA Readiness Check is a self-service to identify technical or functional impacts which have to be considered in SAP S/4HANA conversion or upgrade projects.
S/4HANA Readiness Checks trigger Simplification Item checks to access information about relevance and consistency of simplification items. The findings of these checks get ranked by efforts with low or few days effort, medium effort of few weeks, potentially high effort which depends on customer-specific setup or assessment required for effort determination.
Further outcomes of SAP S/4HANA Readiness Checks are S/4HANA sizing calculations, planned downtimes determination, Fiori app recommendations, Customer Vendor Integration (CVI) analysis, Compatibility Scope check, Financial Data Quality analysis, Add-On Compatibility, active Business Functions, Business Warehouse extractor compatibility checks and Business Process Discovery reports.
Data Volume Management (DVM) is an important technical preparation step to reduce data size with corresponding migration time and costs. DVM considers the S/4HANA data model and HANA tiering options. Sandbox environments offer best practices for technical or functional exploration and test conversion environments.
Additional resource requirements for migration server or shadow system have to be planned. The shadow system consists of two components, shadow instance ABAP stack on the server where SUM is started and the shadow repository on the target database. Shadow systems are created during uptime to reduce downtime processing and time.
The technical SAP Cloud Architecture can be designed with the information collected during the Discovery phase. Cloud architectures have to define strategies for high availability to fulfill SLAs, disaster recovery options, resilient application server landscapes and Defense in Depth security implementations.
System tenancy is implemented deployment specific, multi-tenant for public cloud and single tetant for private cloud (PCE). S/4HANA Public cloud edition is a multi-tenant software as a service (SaaS) offering with multiple self-contained and fully isolated tenant databases. These tenant databases share computing resources, memory, server bandwidth, database system software installation and system administration.
Private Cloud Environments
SAP S/4HANA Private Cloud editions are provisioned by SAP as three tier environments, except XXS size with 2 systems, with a defined amount of application servers. More application servers can be requested with additional costs.
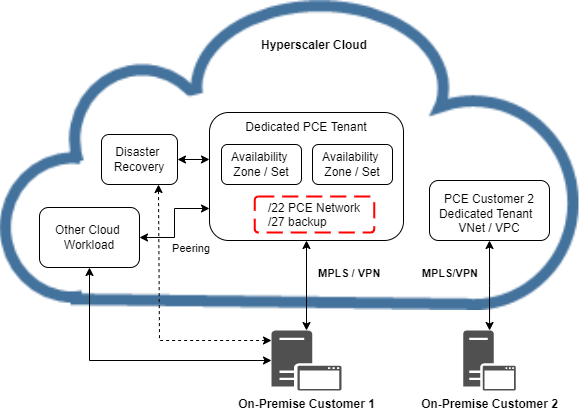
Provisioned HANA databases are scalable with t-shirt sizes proportional to system size and application server amount.
Conversions or migrations can be performed by partners and need temporary storage for Brownfield scenarios.
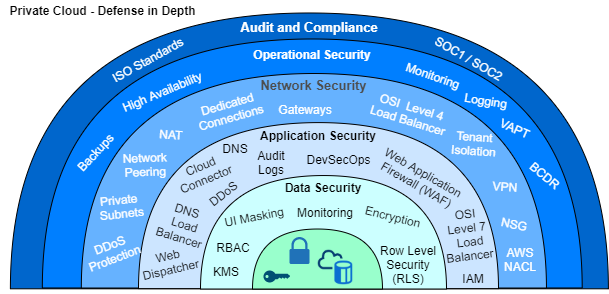
Cloud Defense in Depth
Private Cloud Defense in Depth architectures implement multiple security layers. The operational security layer implements data replication from production for disaster recovery scenarios.
Network Security Layers are realized as dedicated single tenant on the hyperscaler platforms with separated virtual network.
Customers are responsible to establish connectivity with dedicated private network as preferred solution or via VPN. Private IPv4 CIDR address ranges, /22 for PCE network and /27 for backup, have to be non-overlapping with the on-premise network. In addition, IP address 198.18.0.0/15 is reserved for benchmarking / testing by RFC 6890.
Application Security Layer can be implemented within a dedicated zone under the customer internal DNS domain. Web application firewalls offer a defense level to protect against SQL injection and Cross-side-scripting.
The definition of a detailed technical strategy is a key activity in SAP Activate Explore phases of S/4HANA Cloud projects. Extensions have to be specified and planned to solve the requirements found in Fit-to-Standard workshops.
To realize SAP Activate projects, SAP S/4HANA System Conversions convert data and adjust custom code in contrast to new implementation projects with data migration requirements and development of new code.
The SAP Activate realization of S/4HANA Cloud PCE implementations has to implement cloud architecture aspects like Defense in Depth security, scalable workloads, high available and resilient systems, disaster recovery scenarios, performance and data quality.
Cloud architectures, illustrated in the diagram below, enable high availability systems with duplicated ABAP SAP Central Services of ASCS with Message and Enqueue Server, Primary (PAS) and Additional Application Server (AAS), Primary and Secondary databases.
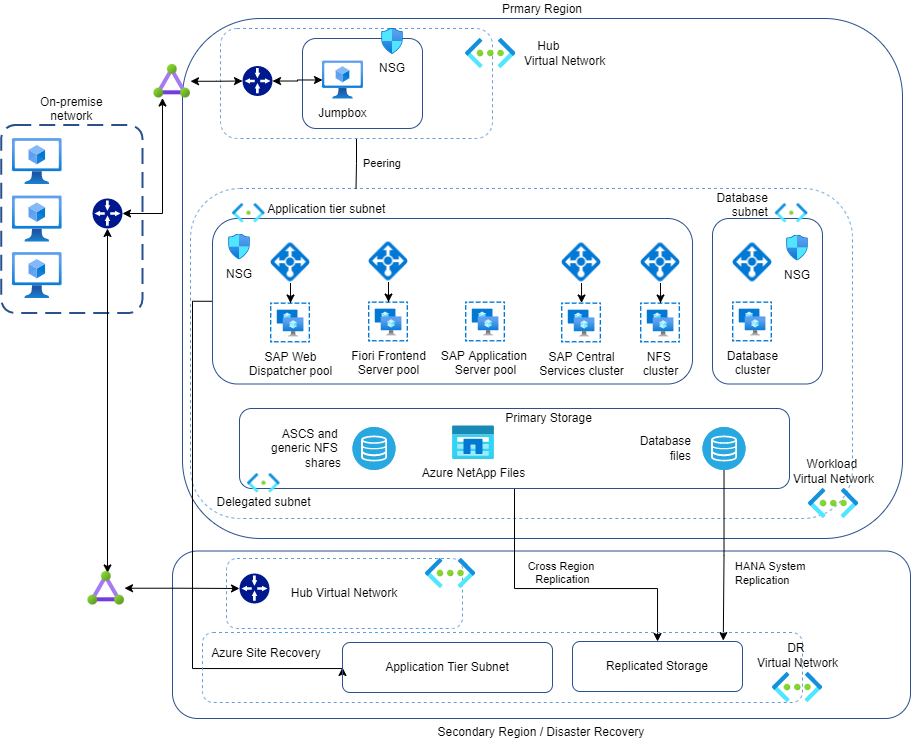
Deployments have to consider the priority and dependency constraints of resources and have to move together bundled migration groups of tightly connected applications.
S/4HANA Fiori Setup
S/4HANA Fiori User Experience has to be enabled with the Fiori Launchpad setup. SAP offers tools for rapid content activation and to manage Fiori apps with content.
The Fiori App Manager offers capabilities to maintain technical catalogs and launchpad app descriptor items. App descriptors are defined as target mapping between app resource and one or more tiles.
Realize System Conversion
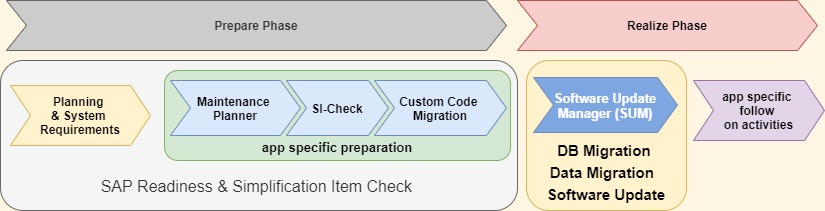
System conversions in S/4HANA Cloud Activate Realize phases shall convert current ERP Systems from Any DB or HANA with minimized disruption for existing business processes and downtime. The SAP Software Update Manager (SUM) tool supports this realization.
SUM technical conversions are performed with Software Update, DB Migration, Data Conversion steps. These steps require a simplification Item consistency check without serious issues.
The Obsolete Data tool cleans up obsolete data, originated from SAP S/4HANA data model simplifications, after conversions. Custom code adjustments can be finalized.
Conversions of financial data take place in Customizing (IMG) activities, followed by functional conversion and cut-over.
SUM Database Migration Option (DMO)
The SUM Database Migration Option (DMO) avoids landscape changes of SID/host name and allows the combination of all relevant steps for the in-place conversion like unicode conversion, update and migration to the target database in one tool. The source database remains consistent to reset the migration procedure.
DMO system conversions to cloud platforms require the installation of a new Primary Application Server (PAS) on the hyperscaler platform.
S/4HANA Downtime Optimization Options
System conversions to cloud target environments have to be planned with transfer times. SAP offers downtime optimization options for conversions or upgrades to reduce processing of table replacements, kernel switch, After Import Methods (AIM), automatically ABAP execution after transport (XPRA) or SPAU modification adjustment.
Downtime-optimized conversions for source HANA or non-HANA DB, have to transfer large tables to targets and execute data conversion or migration partly in uptime.
DMO with system move transfers data with files and offers a parallel mode to run SUM on source and target system with multiple jobs. The DMO parallel mode exports source database in parallel with the import into the target database and performs long-running shadow system activities in uptime. DMO parallel mode does not support downtime optimization and has to be planned with a temporary migration server for file transfers to the cloud.
One-step plain DMO for Azure or AWS transfers data via r3load pipe mode with downtime optimization options and without the need of additional servers.
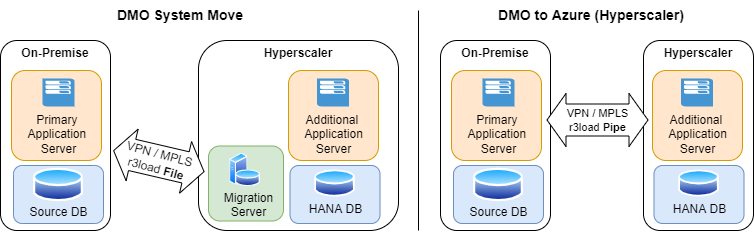
Near Zero Downtime (NZDT) is a service to perform upgrades or migration with source HANA DB to perform DMO on a cloned production system, followed by a delta replay.
The Zero Downtime Option (ZDO) is applicable to perform major release upgrades as well as feature or support package updates.
Realize New Implementation
Some main activities in the S/4HANA Cloud Activate Realize phase for New Implementations are the initial migration data loading and new custom code implementations.
Realize System Copy
System copies of SAP S/4HANA systems require additional resources for HANA offline backups, the upload of source system backups to cloud storage and tools. In a system copy scenario, the Software Provisioning Manager (SWPM) triggers the restore and run post processing.
Realize S/4HANA Cloud
SAP S/4HANA Public and Private Cloud systems offer enhanced options to implement business processes with Responsibility Management, Situation Handling or Workflow implementations.
Responsibility Management determines responsible agents by mappes business processes and team categories categories. Responsibility definitions are name value pairs e.g. plants or purchasing groups to be used for filtering. Tasks can be assigned as functions to team members which are business users with Employee, Service Provider or Freelancer role.
Situation Handling informs end users about current business situations with notifications on the SAP Fiori Launchpad, in-app messages in relevant Fiori apps or via emails. Situations require attention and the triggered notification events enable decisions or automation. Develop custom situation handling templates is part of the extended framework.
Workflows can implement processes with many agents, sequences of tasks or periodically schedules.
Ongoing technical key activities in the SAP Activate Deploy and Run phases for S/4HANA Public or Private Cloud Editions are system extensions and optimizations. Existing extensibility items can be displayed with associations and dependencies in the Extensibility Inventory app.
System optimization and operation has to be implemented with Change Management, Standard Operating Procedures (SOP), Alerting, Knowledge transfer and training.
Monitoring on infrastructure and application level can be implemented with SAP Cloud ALM, SAP Solution Manager or Hyperscaler tools and services.
Default SAP S/4HANA System Landscapes (3SL) are composed of Development, Test and Production systems. 2SL environments are only available for already subscribed S/4HANA Public Cloud systems and S/4HANA Private Cloud XSS sized offerings up to 135 FUE.
SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud subscriptions offer a Starter system for scoping activities with preconfigured Best Practices with sample data to enable the project team and to perform Fit-to-Standard workshops. Starter systems are not configurable during implementation and will be decommissioned approximately 30 days after production system provisioning.
Implementation tasks and monitoring in SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud Deploy and Run phases can be managed with the SAP Cloud ALM (CALM) Implementation Portal.
The Export-/Import Software Collection Fiori app offers capabilities to transfer in-app extensions between S/4HANA Public Cloud system.
SAP notifies customers about half-yearly S/4HANA release upgrades 6
weeks before the upgrade date per Email. Innovation and feature releases
are labeled YYMM.X for
Upgrades with new innovations are executed in two waves. Test systems are are upgraded the first weekend after the Release To Customer (RTC) date, further systems are upgraded the third weekend after RTC. Details can be found in the SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud Upgrade & Maintenance Schedule.
SAP notes can be applied as part of an emergency patch or hotfix.
SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud 3SL environments will be updated first in the Test system, followed by parallel updates of development and production systems. This approach enables developments and configurations during software upgrades without freeze.
Implementation projects can only be transported from development to production with same software version. Furthermore, parallel independent implementation projects with separated transports are supported.
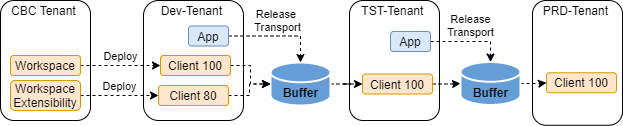
Half-yearly Software upgrades of S/4HANA Public Cloud 3SL environments are separated from content. Content upgrades can be flexible planned before the next major software release.
S/4HANA Public Cloud 3SL environments offer advanced capabilities with regard to client independent development, transportation and quality management. Test systems of 3SL environments offer advanced production like testing with same sizing as productive systems and reduced data masking requirements.
Test systems with preconfigured Best Practices but without sample data have to be requested at the end of the Explore phase.
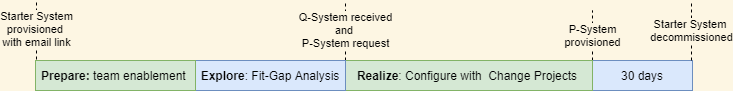
The provisioning of the productive system has to be requested immediately after receiving the active quality system, to ensure that both systems are on the same release level.
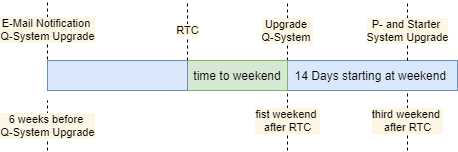
2SL S/4HANA Public Cloud Environments have to plan implementation freeze periods for transportation and update management. Content upgrades are automatically pushed into 2SL environments.
Transports shall be scheduled on Tuesday before Q-System upgrade latest. Imports will be locked latest from Thursday before Q-System upgrade until the end of P-System upgrade.
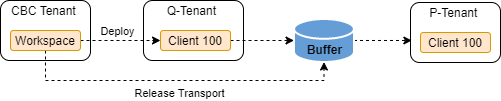
Changes can only be transported from Quality to Production, after both systems are on the same release level and new scope items are activated in both systems.
Change projects can only be created in the quality system after the previous change has been imported to the productive system. Released configuration get queued for transport into the productive system and get automatically imported approx. at 11pm (SAP Note 2707813). Unlike business configuration, extensibility software collections aren't imported automatically.
CBC configuration changes can also be imported immediately in P system with the Import Collection app.
Documented roles and responsibilities for activities are part of the contract between SAP and customers in SAP Activate Deploy and Run phases of RISE with SAP S/4HANA Private Cloud systems. Technical system operations and update installations are performed by SAP on customer request.
One system deployment option is the Cloud Appliance Library (CAL) since SAP S/4HANA 2020 FPS02 with a production-ready deployment option on Microsoft Azure and custom installation plan (non-HA, HA).
SAP Enterprise Support includes collaboration, empowerment, innovation & value realization, mission critical support pillars.
Cloud Application Services (CAS) are offered by SAP with a separate contract and include offerings for e.g. business improvements, application or integration management.
Application Management Services (AMS) can be taken over by partners to manage application changes and deployments, integrations of data or cloud solutions, improvements of business processes, IT operations.
Additional application servers, e.g. for XSS size 2SL environments, can be added with limited scalability, because additional systems have to be subscribed with a minimum time period of several months or permanent.
The SAP Data Volume Management (DVM) offers a Solution Manager launchpad and a Dashboard in the ONE Support Launchpad to minimize growth with data avoidance, summarization, deletion and archiving.
In-app extensions can be deployed with the Configure Software Packages and Register Extensions for Transport apps.
S/4HANA Cloud solutions offer continually innovations with new releases of the S4CORE, ABAP and NetWeaver technology stack. SAP notes are applied as emergency patch or hotfix.
The Release Assessment and Scope Dependency (RASD) tool provides an personalized overview on changes to customers scope at each release. Release related Information is available as SAP Roadmaps and with the What's New Viewer in the SAP Help Portal.
Innovation releases of SAP S/4HANA Private Cloud Editionw (PCE) are labeled YYYY and will be deliverered with two-year release cycle. Feature Pack Stacks (FPS) include non-disruptive features. Support package stacks (SPS) are technically similar to FPS, but contain only corrections and no new functionality.
SPS numbers are consecutive to FPS and contain features of previous FPS. SPS are delivered for previous innovation releases, after new release is available and until the end of mainstream maintenance.
The mainstream maintenance of S/4HANA Private cloud software is limited to 7 years. SAP S/4HANA Private Cloud Editions (SAP PCE) systems have to be upgraded at least every seven year to stay within the mainstream maintenance. Customers could technically skip innovation releases, but this is not a recommended strategy.
S/4HANA Releases with at least 9 months of mainstream maintenance left, are supported conversions to Private Cloud Editions (SAP PCE). Lower S/4HANA releases have limited maintenance policies with the requirement that production systems have to be upgraded to the latest S/4HANA within two weeks after migration.
S/4HANA Cloud Sizing in the Activate Discovery phase requires different strategies to translate business requirements to needed hardware resources like RAM, CPU, Server quantity, bandwidth or IO rate.
S/4HANA Cloud system sizes are mainly defined by full user equivalent (FUE) metrics. One single FUE corresponds to one advanced user e.g. sales order management, 5 core user e.g. production control, maintenance management or 30 self service users e.g. goods movement, physical inventory and to 0,5 licenses. The sum of FUEs is used to calculate the hardware provisioning / HANA size of the S/4HANA Cloud system.
GROW with S/4HANA Cloud public contracts include 100 GB HANA memory, additional memory has to be subscribed separately.
There are different HANA Sizing tools available for the S/4HANA transition paths and deployment scenarios.
The HANA QuickSizer supports greenfield sizing with two sizing models implemented (user or business processes throughput). QuickSizer versions are available HANA-based, HANA-based Cloud and non-HANA based. The HANA-based Cloud version is simplified with only 2 KPIs (HANA RAM, Frontend Network Load). Report /SDF/HDB_SIZING is available for ECC conversions.
HANA-based sizing provides an overview about memory and disk areas to plan Native Storage Extensions (NSE) for warm data.

The peak memory utilization can be checked before rehosting and replatforming of HANA-based systems with tools like:
Fiori and network sizing has to consider different requirements of transactional and analytical processing with maximum concurrent user as input and separated sizing of Fiori frontend server (Embedded/Hub) and Embedded Analytics components.
Appropriate network sizing has to enable Fiori and Embedded Analytics frontend performance. As migration preparation, acceptable system downtimes have to be calculated based on the network connection bandwidth and data transfer times.
SAP Cloud ALM (CALM) is a cloud-based operations platform for cloud centric customers. SAP CALM for Operations manages Detect, Analyse, Correct and Automate lifecycle phases on cloud and hybrid landscapes. Furthermore, problem management is covered by SAP CALM detection with monitoring, routing of alarms and events to resolution with automation and root cause analysis capabilities.
Public cloud services can be registered to SAP CALM as import from System Landscape Information Service (SLIS), via push-enabled registration or manually. Transaction /SDF/ALM_SETUP enables the registration of on-premise systems.
SAP CALM for operations supports intelligent event management with inbound and outbound unification.
SAP CALM Dashboards offer insights on data collected with pull and push mechanisms with monitoring of the areas end-to-end business processes, integrations & exceptions, end-to-end user & performance, jobs & automations and technical healthness of systems or services.
SAP CALM Business Service Management receives cloud system notifications about planned and unplanned downtimes like maintenance, degradations or outages from Cloud Availability Center (CAC).
The SAP CALM Test Management is based on SAP Best Practices content and process-based requirements. SAP CALM tests are lean with simple concepts, agile as soon as possible and targeted scope, process and requirement oriented. SAP CALM offers test traceability during preparation, coverage or execution and automation e.g. with S/4HANA Cloud automation tool.
SAP offers the Fiori app Migrate your Data as tool to migrate data for S/4HANA Public and Private cloud editions. Standard business objects can be migrated with templates and automated mappings, predelivered by SAP, based on customers solution scope. Relevant data migration objects are automatically determined with regard to activated scope items.
Scope items with best practices are available to import standard Migration Objects or custom modelled migration objects. SAP Activate Best Practices describe data migration from File with Scope Item BH5, local or remote Staging Tables with Scope Item 2Q2 and recommend XML file upload for local staging.
SAP S/4HANA public cloud data migrations require the activation of Scope Item 2Q2. Remote database staging integration can be enabled with communication Arrangement Migration Cockpit Integration (SAP_COM_0259) and HANA DBaaS deployment on BTP. Migration users have to own the business role SAP_BR_CONFIG_EXPERT_DATA_MIG and corresponding roles for each migration objects.
Data migrations to SAP S/4HANA Private Cloud systems allow direct connections to source database with staging tables to be filled with suitable tools e.g. SAP Data Services. The migration object modeler tool enables to define migration objects and enhance existing objects.
Further SAP S/4HANA PCE data migration tools are SAP Data Management and Landscape Transformation (DMLT) for selective data transitions, Silent Data Migration Infrastructure (SDMI) which enables migration during uptime or AWS DataSync for fast files and metadata copies.
Some common Data Migration characteristics for both S/4HANA Public and Private Cloud editions are: