SAP S/4HANA Digital Supply Chain solutions like SAP Digital Manufacturing (SAP DM) or SAP EWM Warehouse Management implement intelligent Design-to-Operate processes with S/4HANA Cloud as digital core.
SAP Digital Manufacturing (SAP DM) is offered as SaaS solution on the SAP Business Technology Platform (SAP BTP) Cloud Foundry environment on hyperscaler cloud platforms like Microsoft Azure and Amazon AWS. SAP DM can be integrated vertically into hybrid multi-cloud architectures to realize SAP S/4HANA Digital Supply Chain with cloud components and shop floor processes.

SAP Digital Manufacturing (SAP DM) is composed of execution and insights components. SAP DM execution (SAP DMe) supports manufacturing execution for process and discrete industries. SAP Digital Manufacturing Insights (SAP DMi) transforms business data into value with analytical dashboards and KPIs based on embedded SAP Analytics Cloud (embedded SAC).
SAP Digital Manufacturing Execution (SAP DMe) provides operation capabilities for shop floor manufacturing processes with Production Operation Dashboards (POD) user interfaces to control data from databases or collections.
SAP Digital Manufacturing for execution offers predefined integration options. Business process integrations with S/4HANA Cloud public editions can be implemented without SAP Cloud Integration service subscription. In contrast, SAP DM integrations with On-Premise S/4HANA or SAP ECC require SAP Cloud Connector and SAP Cloud Integration components.

Additionally, the SAP Digital Manufacturing Manage Integration workflows app offers options to customize SAP Cloud Integration behaviors by overriding predefined workflow nodes. Individual integration scenarios can be implemented additionally as cloud integration flows.
Monitoring of integration scenarios with defined message types is offered by the SAP DM Integration Message Dashboard or the Cloud Integration Monitoring Message Processing apps.
Shop floor automation scenarios can be realized with bidirectional integrations of SAP Digital Manufacturing and shop floor solutions, top-down for equipment control and bottom-up to use data collections in SAP DM.
SAP Digital Manufacturing Resource Orchestration (REO) offers short-term shop floor operations planning. Main REO capabilities are shop floor resource management, manual or automatic dispatching of operations to resources and monitoring of manufacturing processes with intuitive visualizations in Gantt charts.
SAP DM Resource Orchestration (REO) schedules scarce resources like work centers, equipments, labor or manufacturing tools on execution level. REO labor management considers workforce availability and qualifications, to schedule based on informed decisions.
In addition, Resource Orchestration offers integration with SAP Manufacturing Execution (ME) which allows to schedule released orders created in SAP ME in REO, transfer schedules dates and resources from REO to SAP ME and to trigger SFC unit creation in SAP ME.
Automated scheduling can be implemented with REO Automatic Dispatching by Heuristics (Scheduling Options) or with Machine Learning (ML) algorithms. Automatic dispatching by Machine Learning (Find Slot Mode) offers infinite and finite (creates slot only if capacity available) scheduling modes with forward scheduling direction. Dispatching of operations to resources can be predicted by machine learning algorithms and controlled by allocated work centers, specified by production supervisors.
SAP DM AI Machine Learning (ML) integrations assist and automate manufacturing processes like Visual Inspections with predicted quality. Visual Inspection scenarios (use-cases), created with the Manage AI/ML Scenarios app, enable operators to review defects with the POD plugin Visual Inspector and to log nonconformance codes (NC) as trigger for automatic corrective actions. During the machine learning (ML) scenario creation, existing models can be uploaded optionally (currently 12/2022 only TensorFlow JavaScript ML models are supported).
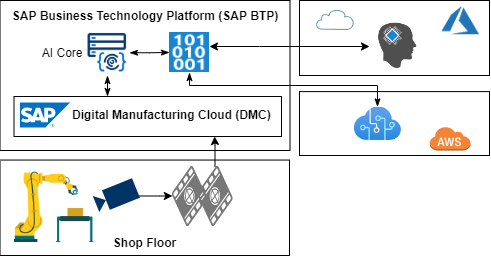
Image classification Machine Learning (ML) models used for Visual Inspections, have to be linked to business processes with plant, material and operation criteria. SAP DM offers APIs to upload inspection log images from cameras on the shop floor to train machine learning (ML) classification models.
The output of trained image classification models automates the nonconformance code (NC) logging in visual inspection scenarios. Active SAP DM visual inspection scenarios can be processed assisted with machine learning (ML) models for training purposes to improve the image classification accuracy.
SAP Digital Manufacturing MES production planning is based on version controlled shop floor routings which determine the sequence of individual operations to finish products. Operation activities describe production processes in detail and optimize shop floor execution with additional functions and information like work instructions.
Master data (e.g. BOMs, routings, materials, resources, work centers) created in SAP DM or with edge components is synchronized continuously. Individual products in discrete manufacturing can be identified and tracked with unique Shop Floor Control (SFC) units throughout the production process. These SFC numbers are used to control production processes, with acquired data collections on the shop floor, with insights for data-driven decisions or automations.
Production orders can be created or released in SAP DM edge or in ERP systems like S/4HANA or SAP ECC. Order status, priority and dates of synchronized orders from ERP to SAP DM can be edited. Build quantities can be adapted with Manage Order app. Order confirmations in SAP Digital Manufacturing for execution (SAP DMe) communicate yield and scrap quantities to SAP ERP or SAP S/4HANA.
SAP DM Production Operator Dashboards (PODs) are the primary SAP DM user interfaces to perform production operations on Shop Floor Control (SFC) units. Some examples of standard PODs are Operation Activities, Production Line or Work Center.
Production Connectivity Models act as digital twins of the physical world and integrate the Machine Model Engine of SAP Asset Performance Management.
SAP Digital Manufacturing offers SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) extensibility options for Business Processes, UI (POD Designer, SAPUI5 apps) and ML/AI scenarios (Visual Inspection).
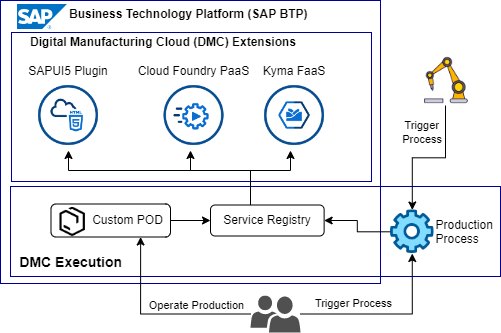
The SAP Digital Manufacturing service registry captures metadata information about all available services offered by SAP DM and integrated systems like e.g. S/4HANA, SAP EWM, shop floor systems, custom extensions, cloud services. These services can be consumed and orchestrated with the SAP DM Design Production Processes app using a graphical design tool and deployed to DMC cloud/egde or Plant Connectivity (PcO) runtime.
SAP DM production processes can automate WIP management with logistics orders to track intralogistics transportation of SFCs and packing units between work centers or resources on the shop floor. As prerequisite, SAP DM Transport Systems have to be created and managed for third-party transport systems, such as Automated Guide Vehicle (AGV) system, for automatic distribution and execution of the logistics orders.
SAP Business Technology Platform (SAP BTP) Kyma FaaS are the recommended approach to implement SAP Digital Manufacturing business process extensions with the BTP Extension Center e.g. as custom logic extension of the SAP DM Manage Next Numbers app for individual numbering patterns of batches, SFCs.
RESTful OData and SOAP services have to be registered as user-defined web servers in the SAP DM service registry. Digital twins of these user-defined physical web servers can be configured and managed in SAP Digital Manufacturing with the Manage Web Servers app.
SAP DM Applications access extensions during runtime within custom production processes (e.g. goods movement with label printing). Extended business processes can be triggered automatically with events (business rules) or timers from outside (subscription, API) or inside SAP DM.
Custom SAP Digital Manufacturing PODs are UI extensions implemented as Fiori components (plugins) to handle individual processes like End-of-Line quality measures with machine learning and data lake cloud services. SAP DM PODs with image overlays, created with the SAP DM Overlay Authoring Tool, can visualize e.g. digital twins of manufacturing lines in the SAP DM Line Monitor plugin for process industries.
BOM Comparison PODs facilitate production variant or version changes in lines (work centers) with preparation lists. These lists compare and visualize BOM information on all levels e.g. quantities of needed materials, category (stock, non-stock), material image.
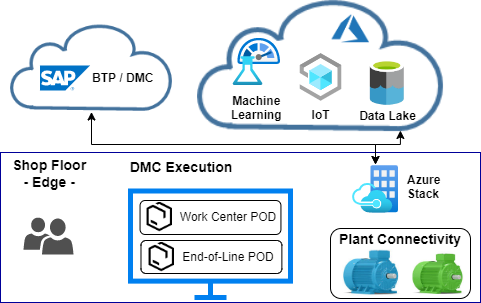
SAP Digital Manufacturing runtime components deployed on the SAP DM edge get connected via SAP Plant Connectivity to the shop floor. SAP DM edge runs decoupled from SAP DM cloud manufacturing execution processes with a upgrade period for edge components three months after the SAP DM cloud release. Edge lifecycle services are offered on the SAP BTP to manage, install and monitor edge components centrally.

Moving computing to the shop floor offers advanced options to solve business continuity requirements. Edge computing on Microsoft Azure brings computation and data storage closer together and reduces dependencies to consistent cloud transfer rates and response times. Decoupled edge operations increase the overall uptime of manufacturing processes because of reduced connectivity dependencies like latency, bandwidth, response times and transfer rates.
Microsoft Azure is currently (03/2023) the only cloud provider which offers advanced SAP Digital Manufacturing Cloud capabilities like Data Engineering and Edge Computing. Running SAP DM Edge workloads on Azure Stack Edge on the shop floor enables faster edge processing and optimized cloud data transfers.
Azure Stack Edge acts as a cloud storage gateway with local cache capability for offline periods (typically 1–2 shifts) and bandwidth throttling (to limit business hours peaks). The edge stack includes a managed Kubernetes environment to run SAP Digital Manufacturing Edge (SAP DMe) on a Kubernetes cluster. SAP DM for edge computing relies on backing services such as persistence, caching and message broker.
SAP Digital Manufacturing for edge computing stores data on the edge only temporarily, for instance when there are production activities for an order. While data is stored on the edge, persistent volumes are used for backing services. Transactionional SAP DM business data gets synchronized with the Business Object Synchronization Service (BOSS) and two-way communication between cloud and edge.
Recommended options to authenticate users on the shop floor are:
SAP Digital Manufacturing for Insights (SAP DMi) offers monitoring, reporting capabilities and data-driven insights to optimize processes based on informed decisions. Process optimizations can be measured based on performance or effectiveness indicators.
SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC) embedded with SAP DMi offers interactive dashboards with standard or custom KPIs with drill-down capabilities to find root causes on different levels (like order, work center or resource).
The SAP DMi Manage Alerts app allows to define conditions and subscriptions for alerts to implement Predictive Quality Management and to initiate corrective actions. Product quality defects can be detected early in production with prediction models using machine learning for Visual Inspection.
Production operators or quality inspectors receiving notifications of type Predictive Quality can view the predictive evaluation results for a specific combination of plant and equipment.